-
CN
-
Service Hotline
+8618129931046 Mr. Liao


Time:2025-12-17 Views:1
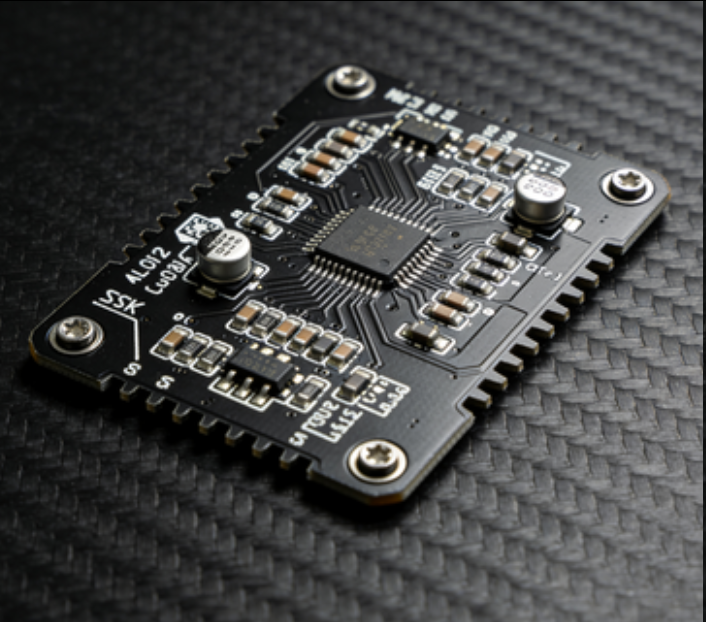
PCB circuit boards for electric scooters (e-scooters) are compact, rugged components that control core functions like motor operation, battery management, and user interaction—tailored to the low-to-medium power (250W–1200W) needs and urban commuting use case of e-scooters. These PCBs prioritize space efficiency, durability, and energy optimization to support short-to-medium range travel (10–40 km per charge).
Key functional modules include: a motor controller (with MOSFETs to regulate brushless DC motor speed based on throttle input), a battery protection circuit (monitoring 36V/48V lithium-ion packs to prevent overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits), and a user interface interface (connecting to LED displays for speed, battery level, and error codes). PCBs use standard FR-4 material (Tg ≥150°C) with 1–2 oz copper layers, and adopt a 2–4 layer design to fit the e-scooter's tight chassis (typically 60mm×120mm or smaller).
Design considerations include waterproofing (IP65–IP67 rating) to withstand rain and splashes, and vibration resistance (reinforced solder joints) to handle rough urban roads. Many e-scooter PCBs integrate regenerative braking circuits to recharge the battery during deceleration, extending range. For example, PCB boards for Segway Ninebot e-scooters feature intelligent power distribution to balance motor performance and battery life. These PCBs are critical for e-scooter reliability—ensuring smooth acceleration, consistent braking, and long-term durability—making them essential for manufacturers targeting consumer and shared mobility markets.