-
CN
-
Service Hotline
+8618129931046 Mr. Liao


Time:2025-08-06 Views:1
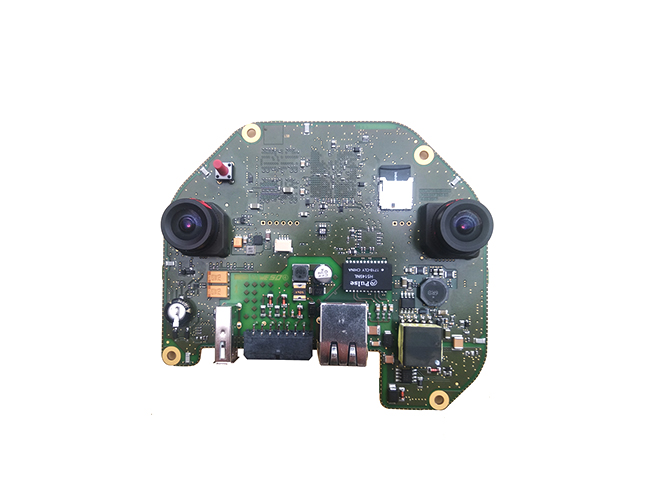
Industrial automation PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) are the backbone of automated manufacturing systems, providing the electrical connectivity and signal processing required for machinery, robotics, and control systems to operate with precision and reliability. These PCBs are designed to withstand harsh industrial environments, including extreme temperatures (-40°C to 85°C or higher), vibration, dust, and electromagnetic interference (EMI), making them distinct from consumer electronics PCBs.
One of the key design considerations for industrial automation PCBs is robust material selection. Substrates with high glass transition temperatures (Tg), such as FR-4 with Tg values above 170°C, are commonly used to prevent warping under thermal stress from components like power resistors or motor drivers. Heavy copper layers (2 oz or more) are often incorporated to handle high currents, which is essential for driving motors, actuators, and other power-hungry devices in automation systems.
Signal integrity is critical in industrial automation, where PCBs must transmit high-speed control signals (e.g., Ethernet/IP, PROFINET, or Modbus) between sensors, controllers, and actuators with minimal latency. To achieve this, designers use controlled impedance traces, ground planes, and shielding to reduce crosstalk and EMI. Additionally, industrial PCBs often feature redundant power paths and protection components (such as TVS diodes, fuses, and transient suppressors) to prevent damage from voltage spikes or power surges, which are common in factory environments.
Component selection is another vital aspect. Industrial automation PCBs use ruggedized, industrial-grade components with extended temperature ranges and high reliability ratings (e.g., components meeting IEC 61010 standards for industrial control equipment). Surface-mount technology (SMT) is widely adopted for compactness, but through-hole components may be used for high-power or high-vibration applications to ensure mechanical stability.
These PCBs are found in a wide range of industrial automation equipment, including programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), robotic arms, conveyor systems, and quality inspection machines. Their ability to integrate analog sensors, digital control circuits, and power management modules into a single board simplifies system design and improves reliability. As industrial automation moves toward Industry 4.0, these PCBs are increasingly incorporating IoT capabilities, with embedded processors and communication modules to enable real-time data analytics and remote monitoring, further enhancing productivity and efficiency in smart factories.